- 0 Comments
- Liver Cancer, Liver Diseases
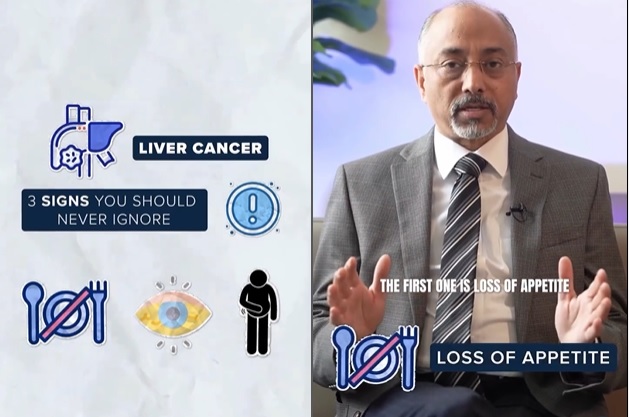
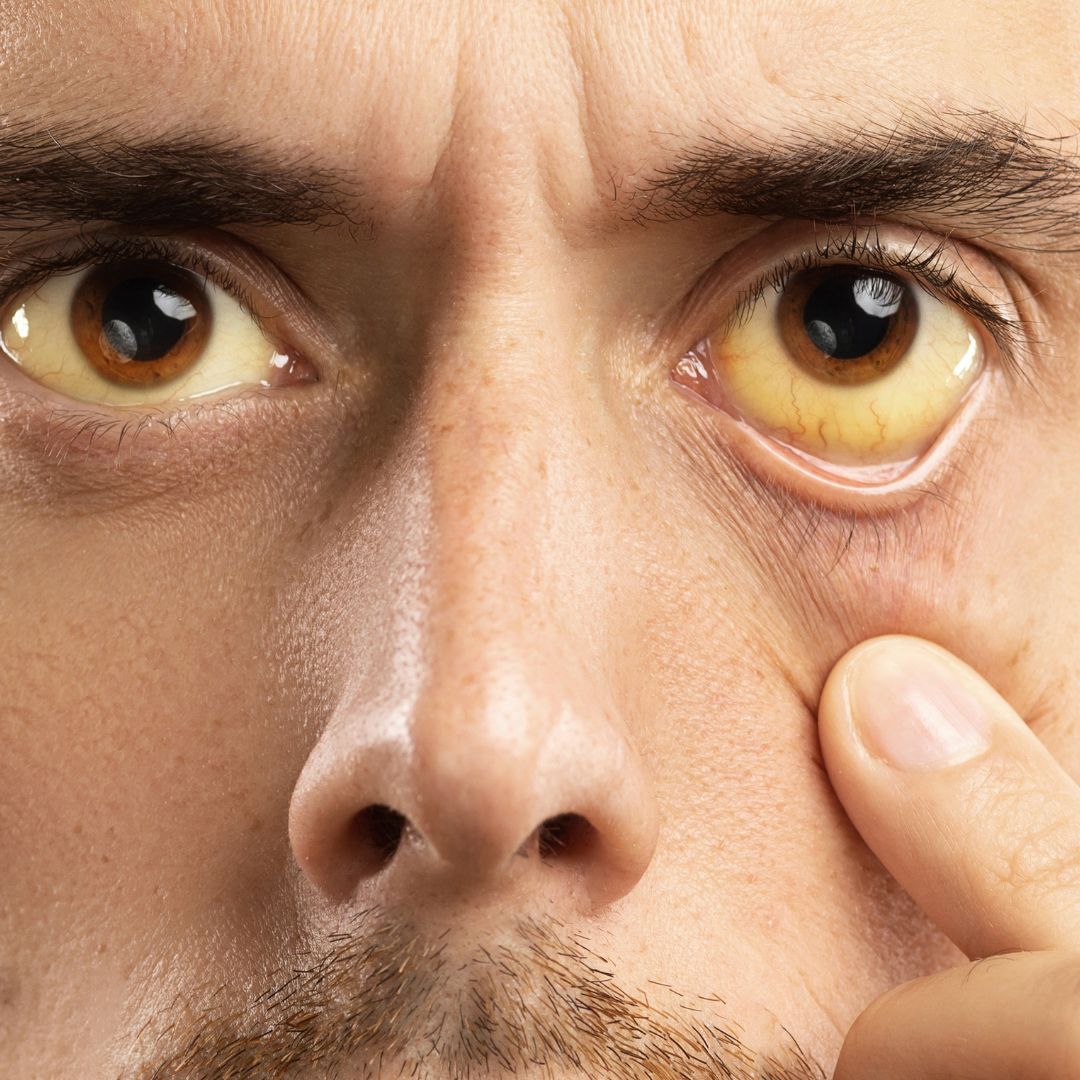
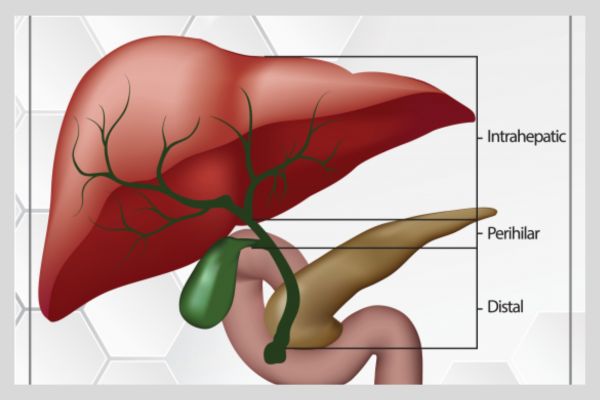
Types of Cholangiocarcinoma Cholangiocarcinoma is classified based on where it occurs in the bile ducts: Symptoms of Bile Duct Cancer Symptoms may be subtle in early stages, but commonly include: At King’s College Hospital Dubai, Dr. Rakesh Rai, a globally trained HPB (Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary) and liver transplant surgeon, offers advanced care for patients with cholangiocarcinoma. He leads a team […]